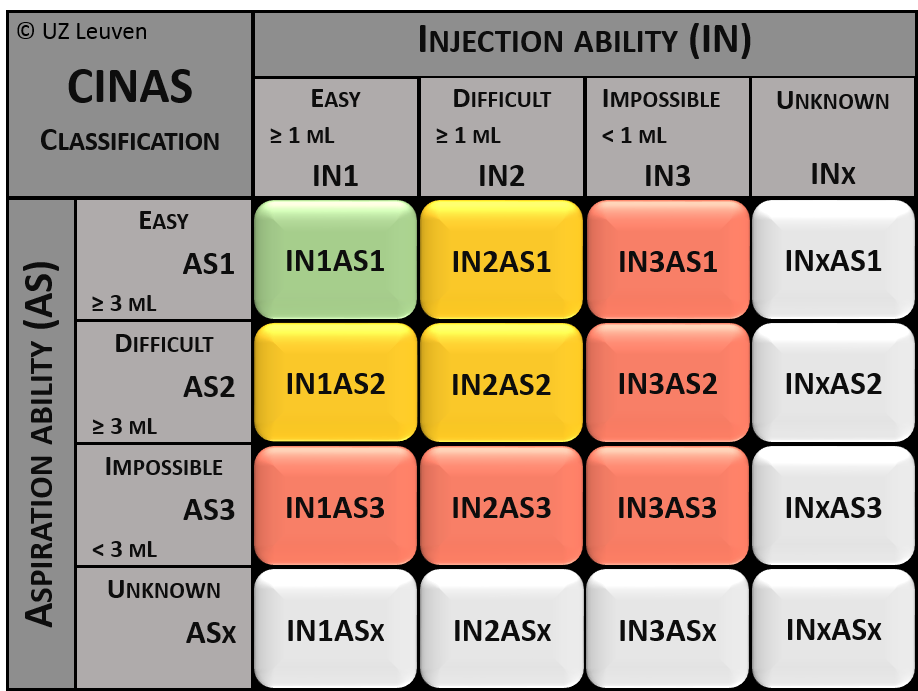
CINAS classification scheme
In other languages: Français, Deutsch, Italiano, svenska, português, polskima and 中文.
What is CINAS?
The Catheter INjection and ASpiration (CINAS) is a classification instrument for intravenous catheter function. It is based on the evaluation of both the injection and aspiration abilities of the catheter.
A catheter malfunction is defined as any situation where the injection or aspiration ability is no longer easy but has become difficult or impossible.
The catheter function is classified on a 1 to 3 scale.
- 1 = easy
- 2 = difficult
- 3 = impossible
- X = unknown
Some examples
- A catheter with an easy injection ability, where however blood aspiration is impossible, also known as “withdrawal occlusion”: IN1AS3.
- Along the CINAS, a well-functioning catheter with easy injection and aspiration abilities: IN1AS1.
- A totally blocked catheter where both injection and aspiration are impossible: IN3AS3.
Clinical practice examples: test yourself
- Injection is easy but when you try to get blood aspirated, there is only a little amount of pink coloured fluid in the extension set. You get brisk blood return after additional injection of flushing solution (0.9% Sodium Chloride) and asking the patient to change its chest, arm and/or head position. At the end you get sufficient blood for finalising the blood sampling.
CINAS classification=IN1AS2
More information. - You start with a blood sampling procedure through an implantable port. When you start flushing you notice that you can inject easily and , also aspirate blood easily. However when you finish to fill the second vacutainer® tube, the blood stops flowing whatever you try (e.g. extra flushing, access the totally implantable port with a longer Huber needle…). Finally, you decide to fill the remaining vacutainer tubes via peripheral vein puncture.
CINAS classification=IN1AS3
More information. - You have to administer an IV push medication through an injection port the administration set. Injection is tight, you test the blood return which is impossible.
CINAS classification=IN2AS3
More information. - You access an implantable port for the delivery of IV chemotherapy and there is no blood sampling required. It is easy to inject, you try to confirm the blood return, which is negative. You take some actions in an attempt to get blood return, at the end you get 2 ml of blood.
CINAS classification=IN1AS3
More information. - You access an implantable port and there is no blood sampling required. It is easy to inject, you try to aspirate but you have no blood return. You take some actions in an attempt to get blood return, at the end you get 3 ml of blood.
CINAS classification=IN1AS2
More information. - You just walk in a patient’s room and you see an empty infusion bag. The administration set, which is attached to the patient’s central venous catheter is completely filled with blood. You try to flush but it is impossible , you try to aspirate but you get no blood return.
CINAS classification=IN3AS3
More information. - You just walk in a patient’s room and you see an empty infusion bag. The administration set, which is attached to the patient’s central venous catheter is completely filled with blood. You try to flush but it is impossible, you try to aspirate but you get no blood return. You start thrombolytic treatment and after a few minutes you can inject 1.5 ml of the thrombolytic drug. This injection was possible however it was not easy. You try to aspirate 3 ml of blood which went easily and you get brisk blood return. You tried to inject again, however, this remains difficult.
CINAS classification=IN2AS1
More information. - You just walk in a patient’s room and you see an empty infusion bag. The in administration set, which is attached to the patient’s central venous catheter is completely filled with blood. You try to flush but it is impossible , you try to aspirate but you get no blood return. You start thrombolytic treatment and after a few minutes you can inject 1.5 ml of the thrombolytic drug. This injection was possible however it was not easy. You try to aspirate 3 ml of blood and this was possible however, you could only aspirate the blood with a lot of efforts with a syringe.
CINAS classification=IN2AS2
More information. - You access an implantable port and it is easy to inject, you try to aspirate but you have no blood return. You take some actions in an attempt to get blood return, at the end you get 3 ml of blood.
CINAS classification=IN1AS2
More information. - You have to draw blood via a tunnelled catheter and fill 4 Vacutainer® tubes. The flushing wit 0.9% Sodium Chloride is easy. You start filling the blood tubes but after 2 tubes, blood aspiration stops. You tried to aspirate the blood with a syringe and you managed to fill the 2 other tubes.
CINAS classification=IN1AS2
More information. - You noticed a slow infusion rate and certainly below the prescribed infusion flow rate. You try to obtain a higher flow rate. However, you observed consistently a low flow. Blood aspiration ability was not evaluated.
CINAS classification=IN2ASX
More information.
Research publication
Read the first page of the article 'Diagnostic accuracy of the Catheter Injection and Aspiration (CINAS) classification for assessing the function of totally implantable venous access devices' (pdf).
Interested in the full article? Mail to Godelieve Goossens.